Unblinding the OS to Optimize User-Perceived Flash SSD Latency
Abstract
In this paper, we present a flash solid-state drive (SSD) optimization that
provides hints of SSD internal behaviors, such as device I/O time and buffer
activities, to the OS in order to mitigate the impact of I/O completion
scheduling delays. The hints enable the OS to make reliable latency
predictions of each I/O request so that the OS can make accurate scheduling
decisions when to yield or block (busy wait) the CPU, ultimately improving
user-perceived I/O performance. This was achieved by implementing latency
predictors supported with an SSD I/O behavior tracker within the SSD that
tracks I/O behavior at the level of internal resources, such as DRAM buffers
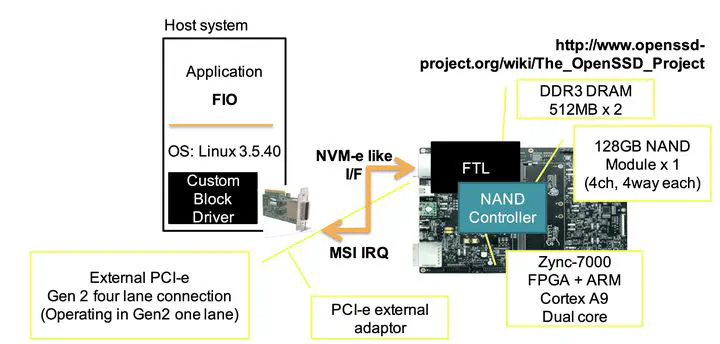
or NAND chips. Evaluations with an SSD prototype based on a Xilinx Zynq-7000
FPGA and MLC flash chips showed that our optimizations enabled the OS to mask
the scheduling delays without severely impacting system parallelism compared
to prior I/O completion methods.
Type
Publication
8th USENIX Workshop on Hot Topics in Storage and File Systems